Radware’s cyberthreat intelligence (CTI) team assesses DDoS attacks targeting the digital infrastructure of the Paris 2024 Olympics.
DownloadOverview
- Radware’s cyberthreat intelligence (CTI) team assesses DDoS attacks targeting the digital infrastructure of the Paris 2024 Olympics.
- Intelligence suggests hacktivists will create chaos by focusing on high-visibility targets like ticketing, streaming and betting platforms to advance their political agendas.
Background
- In 2016, threat groups targeted public-facing properties and organizations affiliated with the Rio Olympic Games. They launched sustained, sophisticated, large-scale DDoS attacks that reached up to 540 Gbps and were fueled by an internet of things (IoT) botnet coupled with a few other botnets. These Olympics-related DDoS attacks used UDP reflection/amplification vectors to power a large portion of the attack volume. DNS, chargen, ntp, and SSDP were the main vectors, but direct UDP packet-flooding, SYN-flooding, and application-layer attacks targeting web and DNS services were also observed. The 2020 Tokyo Olympics witnessed an unprecedented 450 million attacks. For the 2024 Paris Games, the onslaught could be even worse.
- In June 2024, Russian hacktivist groups HackNeT and the Cyber Army of Russia Reborn claimed a series of DDoS attacks against French websites (see Figures 1-4), including those of the La Rochelle International Film Festival and the Grand Palais. The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn, which Mandiant linked to the Kremlin, referred to these attacks as "training," suggesting they were testing their capabilities in preparation for larger-scale disruptions during the Olympics.
 Figure 1: NoName057(16) Telegram post claiming attack on French sites as a warmup for attacks during the 2024 Paris Olympics
Figure 1: NoName057(16) Telegram post claiming attack on French sites as a warmup for attacks during the 2024 Paris Olympics 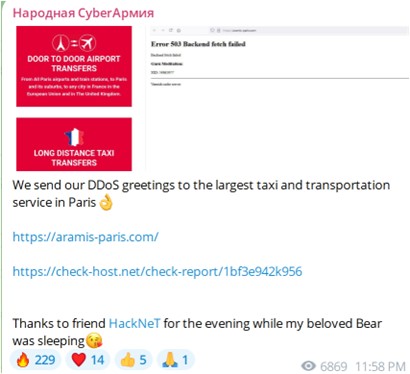 Figure 2: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post claiming attack on the largest Taxi and Transportation service in Paris
Figure 2: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post claiming attack on the largest Taxi and Transportation service in Paris
Hacktivist Targeting Criteria
Hacktivists strategically select targets for maximum impact and visibility …
- Impact: Crippling services that generate a media firestorm and widespread frustration.
- Timing: Striking at peak moments to amplify disruption while minimizing resource needs.
At-risk sectors and industries include …
- Olympics logistics and operations:
- Ticketing systems: Responsible for selling and distributing tickets to events.
- Venue access control: Manage entry and security at Olympic facilities.
- Hotel booking platforms: Handle accommodations for athletes, officials and spectators.
- Streaming and media:
- Official Olympics streaming platforms: Provide live and on-demand coverage of events to global audiences.
- Major broadcaster streaming services: Offer exclusive content and commentary to subscribers.
- Sports betting: Online sportsbooks allowing wagers on Olympic events and outcomes.
- Financial services: Payment processors facilitating transactions for tickets, merchandise and other Olympics-related purchases.
- Tourism and hospitality:
- Airline booking systems: Manage travel arrangements for athletes, officials and spectators.
- Hotel reservation platforms: Handle room bookings and guest services.
- Travel websites and apps: Provide information and services for Olympics-related travel.
- Olympics-specific digital services:
- Official Olympics mobile apps: Provide real-time event information, schedules, results, and updates to attendees and fans, serving as a central hub for engagement.
- Volunteer coordination systems: Used to recruit, train, schedule and manage the large volunteer workforce supporting Olympics operations across venues and events.
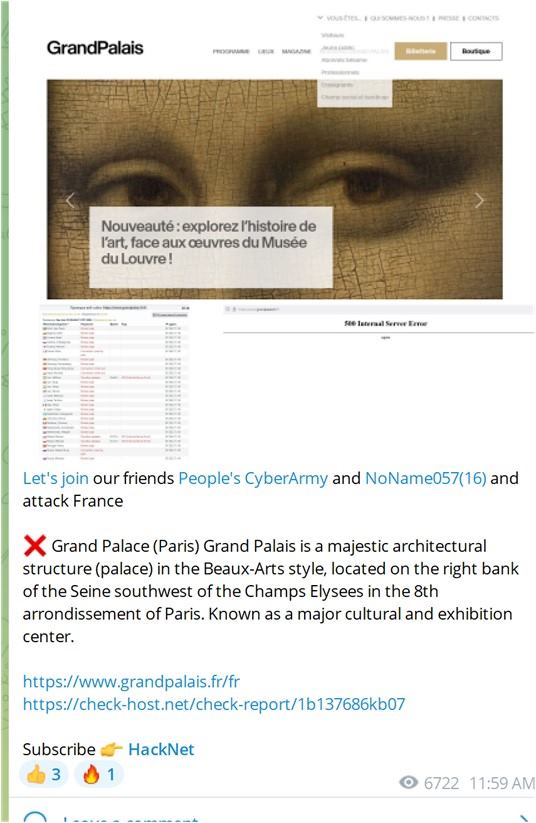 Figure 3: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post calls to join them and NoName and attack Franch Bank
Figure 3: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post calls to join them and NoName and attack Franch Bank
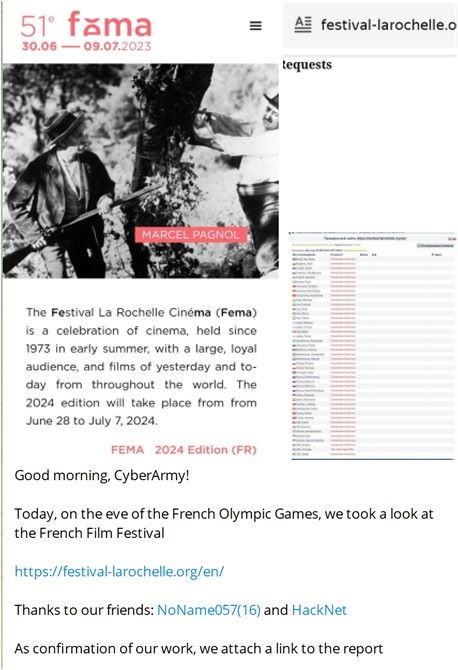 Figure 4: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post clamming attack on the French Film Festival
Figure 4: The Cyber Army of Russia Reborn Telegram post clamming attack on the French Film Festival
Potential Impact
- Even a momentary outage can quickly spiral into a global media crisis, playing right into the hacktivists' hands.
- Risks include serious safety threats, diplomatic firestorms, and long-term damage to the Olympic brand and partners.
Reasons for Heightened Concern
- Geopolitical tensions:
- The war between Russia and Ukraine, tension between NATO and Russia upon new members joining the organization, and the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in Gaza are both at critical stages that could determine the future of the Middle East and Europe. These conflicts fuel hacktivist groups, placing significant pressure on them to act.
- Hacktivists' innovative capabilities:
- DDoS tools have entered a new era with AI-powered CAPTCHA-solving capabilities, enabling hacktivists to unleash staggering attack traffic volumes while staying hidden.
- Traditional defenses will see these advanced threats as human traffic and won’t check it.
Staying Protected
EFFECTIVE DDOS PROTECTION ESSENTIALS
Intelligence on Active Threat Actors – High fidelity, correlated and analyzed data for preemptive protection against currently active known attackers
Behavioral-Based Detection - Quickly and accurately identify and block anomalies while allowing legitimate traffic through
Real-Time Signature Creation - Promptly protect against unknown threats and zero-day attacks
Cybersecurity Emergency Response Plan - A dedicated emergency team of experts who have experience with Internet of Things security and handling IoT outbreaks
Hybrid DDoS Protection – Use on-premise and cloud DDoS protection for real-time DDoS attack prevention that also addresses high-volume attacks and protects from pipe saturation
For further network and application protection measures, Radware urges companies to inspect and patch their network to defend against risks and threats.
EFFECTIVE WEB APPLICATION SECURITY ESSENTIALS
Low false positive rate - using negative and positive security models for maximum accuracy
Auto-policy generation - capabilities for the widest coverage with the lowest operational effort
Bot protection and device fingerprinting - capabilities to overcome dynamic IP attacks and achieve improved bot detection and blocking
Full OWASP Top-10 – coverage against defacements, injections, etc.
Flexible deployment options – on-premises, out-of-path, virtual or cloud-based
Securing APIs - by filtering paths, understanding XML and JSON schemas for enforcement, and using activity tracking mechanisms to trace bots and guard internal resources
LEARN MORE AT RADWARE’S SECURITY RESEARCH CENTER
To know more about today’s attack vector landscape, understand the business impact of cyberattacks, or learn more about emerging attack types and tools, visit Radware’s Security Research Center. Additionally, visit Radware’s Quarterly DDoS & Application Threat Analysis Center for quarter-over-quarter analysis of DDoS and application attack activity based on data from Radware’s cloud security services and threat intelligence.